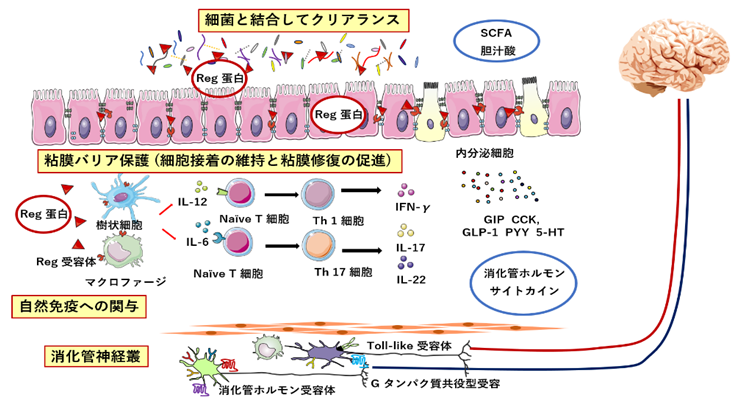
腸内細菌叢の攪乱と消化管微小炎症における Reg ファミリー蛋白の役割
情報更新日 2023年7月31日
シーズ情報
キーワード
Regenerating gene (Reg) 蛋白
分野
消化管内科学、炎症性腸疾患 (IBD) 、過敏性腸症候群 (IBS)
概要
我々は、Regenerating gene (Reg) 蛋白が消化管粘膜の再生・修復に役割を果たすことを明らかにしたが、近年、抗菌ペプチドとして粘膜防御機序で重要な役割を果たす可能性が示唆され改めて注目されている。一方、腸内細菌叢の攪乱 (dysbiosis) が 機能性消化管障害 (FGID) や 炎症性腸疾患 (IBD) などの消化管疾患のみならず精神・代謝疾患の病態にも深く関することが明らかになり注目されている。
本研究では、FGID と寛解期の IBD に生じる過敏性腸症候群 (IBS) 様症状の病態解明を念頭におき、種々の動物モデル (Reg 遺伝子改変マウス、抗菌薬および高脂肪食負荷による dysbiosis モデル、母子分離および社会的敗北ストレスモデル) を用いて腸内細菌、粘膜バリア機能および免疫応答における Reg family 蛋白の機能解析を行い、腸内細菌叢の攪乱と消化管微小炎症における Reg family 蛋白の役割を明らかにすることを目的として研究を進めている。
また、上記の基礎研究に加えてヒト臨床研究では、粘膜バリア機能を指標とした消化管粘膜傷害の定量的検査法の開発も進めている(特許出願準備中)。上記モデル動物の研究と合わせ、FGID、IBD、メタボリック症候群、薬物起因性消化管障害などの病態や発症機序の解明に寄与するものと考えている。
FGID; functional gastrointestinal disorder
IBD; inflammatory bowel disease
IBS; irritable bowel syndrome
何が新しいか?
Reg family 蛋白の腸管自然免疫機構における重要性は近年注目され始めたばかりであり、その機能解析から臨床応用を目指す本研究は先端的である。
IBDの腸管粘膜で最も強発現する遺伝子としてReg family 遺伝子が同定され、Reg family 蛋白の作用/発現から治療薬、バイオマーカーとしての可能性がある。
また、消化管やその他の領域の腫瘍でも強発現することを報告した。さらに、 Reg 蛋白の腫瘍細胞に対する作用を明らかにし、癌治療における治療やバイオマーカーとしての可能性を示している。
他の研究に対する優位性は何か?
消化管組織におけるReg蛋白の機能解析を世界に先駆けて行った研究であり、以下の様な強みがある。
- 関連するヒトおよびモデル動物の研究業績やデータの蓄積が豊富である。
- Reg family の様々な遺伝子改変モデルを有しており、今後さらに研究を大きく発展させていく準備ができている。
- 本学はIBD患者が集まる high volume センターであり、炎症性腸疾患領域における研究テーマの発展が見込まれる。
- また、腫瘍性疾患においては、上述のように癌治療における標的分子になる可能性、抗癌剤治療における効果判定や予後予測マーカーとして臨床応用できる可能性を追求する上で、本学には多くの抗癌剤治療患者数がありるため、この点でも研究テーマの発展が見込まれる。
どのような課題の解決に役立つか?
IBDやIBSにおける種々の課題解決に役立つ。
【創薬】
- Reg family 蛋白が腸管自然免疫機構において抗菌ペプチドとして抗炎症作用を示すのではないかと注目されている。抗炎症作用があるなら、IBDや薬物起因性粘膜傷害における治療薬候補になる。
- また、逆に、Reg family 蛋白が炎症を惹起させるトリガーになっている可能性もある。その作用を抑える抗体などの阻害剤がIBDや薬物起因性粘膜傷害における治療薬候補になる可能性がある。
【診断・検査】
- IBDでReg family 蛋白が著しく強発現していることは明白であり、少なくとも疾患における病勢や治療効果判定のマーカーになる可能性がある。
- IBS様症状では、客観的な評価法の確立が課題であり、新たな粘膜バリア機能を指標とした消化管粘膜傷害の定量的検査法が課題解決に繋がる可能性がある。
他への応用・展開の可能性
Reg family 蛋白は炎症性疾患のみならず、消化管やその他の領域の腫瘍でも強発現することを、我々だけでなく多くの施設が報告してきた。
我々は Reg 蛋白が腫瘍細胞の抗アポトーシス能獲得に役割を果たしていることを明らかにし、腫瘍細胞に対する抗癌剤の作用効果に影響を与えることを示唆しました。この点から、Reg family 蛋白は癌治療における標的分子になる可能性がある。また、少なくとも、抗癌剤治療における効果判定や予後予測マーカーとして臨床応用できる可能性がある。
関連する特許
発明の名称:消化管粘膜傷害の定量的検査法(特許出願準備中)
関連する論文等
- Sekikawa A, Fukui H, et al. REG Iα protein may function as a trophic and/or anti-apoptotic factor in the development of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2005; 128: 642-653.
- Sekikawa A, Fukui H, et al. Possible role of REG Iα protein in ulcerative colitis and colitic cancer. Gut 2005; 54: 1437-1444.
- Nanakin A, Fukui H, et al. Expression of the REG IV gene in ulcerative colitis. Lab Invest 2007; 87: 304-314.
- Fukui H, et al. DMBT1 is a novel gene induced by IL-22 in ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2011; 17: 1177-1188.
- Sun C, Fukui H, et al. Expression of Reg family genes in the gastrointestinal tract of mice treated with indomethacin. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2015, 308: G736-744.
- Kitayama Y, Fukui H, et al. Role of regenerating gene I in claudin expression and barrier function in the small intestine. Transl Res 2016, 173: 92-100.
- Fukui H, et al. Effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 on the relationship between gut microbiota profile and stress sensitivity in maternally separated rats. Sci Rep 2018, 8: 12384
- Fukui H, et al. Role of gut microbiota-gut hormone axis in the pathophysiology of functional gastrointestinal disorders. J Neurogastroenterol Motil 24:367-386, 2018.
- Xu X, Fukui H, et al. Alteration of GLP-1/GPR43 expression and gastrointestinal motility in dysbiotic mice treated with vancomycin. Sci Rep 2019, 9: 4381.
- Xu X, Fukui H, et al. The link between type III Reg and STAT3-associated cytokines in inflamed colonic tissues. Mediators Inflamm 2019; 7859460.
- Ran Y, Fukui H, et al. Alteration of colonic mucosal permeability during antibiotic-induced dysbiosis. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21: 6108.
- Fukui H, et al. Usefulness of machine learning-based gut microbiome analysis for identifying patients with irritable bowels syndrome. J Clin Med, 2020, 9: 2403.
- Ebisutani N, Fukui H, et al. Decreased colonic guanylin/uroguanylin expression and dried stool property in mice with social defeat stress. Front Physiol 2020; 11: 599582.
- Nishimura H, Fukui H, et al. Role of the β-catenin/REG Iα axis in the proliferation of sessile serrated adenoma/polyps associated with Fusobacterium nucleatum. Pathogens 2021; 10: 434.
- Sun C, Fukui H, et al. The Potential role of REG Family proteins in inflammatory and inflammation-associated diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 7196.
- Nakanishi T, Fukui H, et al. Effect of a high-fat diet on the small-intestinal environment and mucosal integrity in the gut-liver axis. Cells 2021; 10: 3168.
- Wang X, Fukui H, et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 has a preventive effect on the acceleration of colonic permeability and M1 macrophage population in maternally separated rats. Biomedicines 2021; 9: 641.
研究者情報
| 氏名 | 福井 広一 |
|---|---|
| 所属 | 医学部 消化器内科学 |
| 専門分野 | 消化管内科学、炎症性腸疾患 (IBD) 、過敏性腸症候群 (IBS) |
| 学内共同研究者 | ― |
| 関連リンク | 講座紹介HP |
企業との協業に何を期待するか?
製薬企業や診断薬企業との協業により、以下の様な共同研究の実施などを期待する。
- モデル動物や臨床検体を用いた、バイオマーカーや創薬標的の探索研究
- 製薬企業が保有する機能性ディスペプシア、過敏性腸症候群、IBD、メタボリック症候群、薬物起因性消化管障害などの治療候補物質の検証研究
- 新たな粘膜バリア機能を指標とした消化管粘膜傷害の定量的検査法を基にした、上記疾患に対する治療候補物質の探索
本研究の問い合わせ先
兵庫医科大学 大学事務部 研究推進課
E-mail: chizai@hyo-med.ac.jp
Tel: 0798-45-6488

 研究シーズ集
研究シーズ集