Awards
Selected for the 2024 Japan Society of Cerebral Circulation and Metabolism Evidence Creation and Basic Research Promotion Research (Takayuki Nakagome, Director of Institute for Advanced Medical Sciences)
The research of Professor Takayuki Nakagome, head of Laboratory of Neural Repair and Regeneration Institute for Advanced Medical Sciences, has been selected as a certified research (basic research) by the Evidence Creation and Basic Research Promotion Committee of the Japanese Society for Cerebral Circulation and Metabolism. The award ceremony was held at the 67th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society for Cerebral Circulation and Metabolism on November 1st, and Nakagome gave a lecture on the results of his research.
Name of the awarding organization
Japanese Society for Cerebral Circulation and Metabolism
Research topic
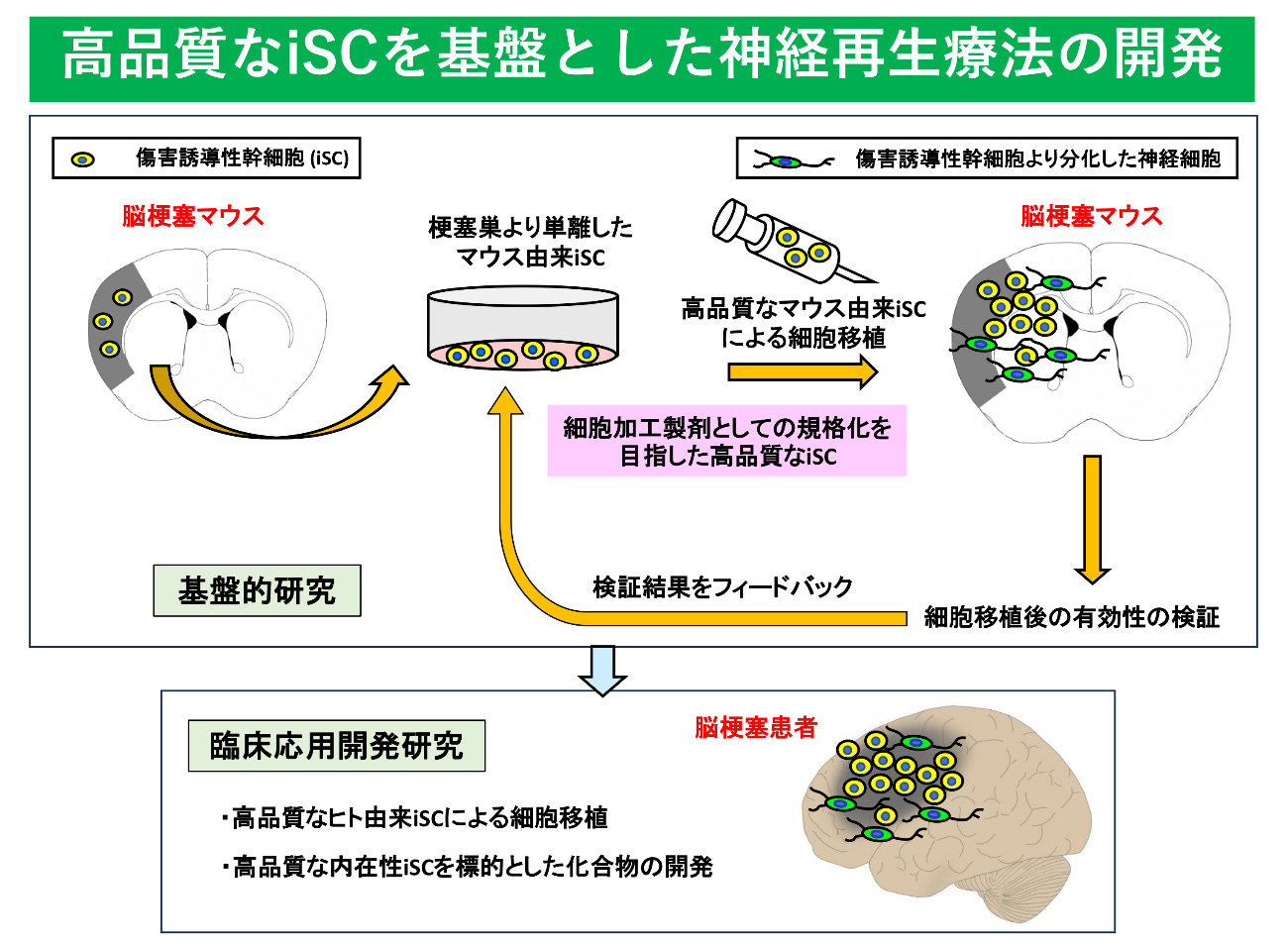
Fundamental research aimed at developing innovative new neural regeneration therapies using high-quality injury-induced stem cells
Research Overview
Cerebral infarction is a disease that presents neurological deficits due to ischemia, and often leads to complications such as paralysis and speech disorders, making it a major cause of bedriddenness. The associated social loss is enormous, and the development of an effective treatment is an urgent task.
Laboratory of Neural Repair and Regeneration at Institute for Advanced Medical Sciences at our university was the first in the world to report the existence of endogenous stem cells (injury/ischemia-induced Stem/Progenitor Cells: iSCs) that are specifically induced during brain injury and pathological conditions (Neural Regen Res, 20, 797-798, 2025).
Recently, we conducted a preclinical study in which human-derived iSCs isolated and cultured from cerebral infarction patients were transplanted into cerebral infarction mice, and in a collaborative study with the Department Department of Neurosurgery at our university, we demonstrated that cell transplantation with human-derived iSCs improves neural function through the activation of endogenous neural stem cells and the reconstruction of neural networks (Stem Cells Transl Med, 12, 400-414, 2023). These results suggest that cell therapy using iSCs may become a useful new treatment for brain injuries such as cerebral infarction in the future.
Unlike known transplant candidate cells, iSCs are endogenous stem cells induced in vivo during brain injury pathology, so they can be expected to be applied not only to cell transplantation but also to the development of treatments targeting iSCs present in vivo during pathology. However, through previous research, it has become clear that there are several subtypes of iSCs, and it has not been clarified which subtype of iSC is most useful for improving neurological deficits. Therefore, in this research project, we will conduct basic research using iSCs (high-quality iSCs) that are most likely to be effective in nerve regeneration and improvement of neurological deficits among iSCs with various cellular characteristics, and promote the development of innovative new nerve regeneration therapies for cerebral infarction (see figure below).