Achievements
Alcoholism is the leading cause of liver cirrhosis in Japan: Nationwide survey reveals that causes of chronic liver disease are progressing from viral to non-viral
Professor Enomoto Tairayuki of the Department of Gastroenterology (Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Internal Medicine) and his colleagues conducted a nationwide survey on the causes of liver cirrhosis, which is conducted by the Japan Society of Hepatology every five years, in 2023, following on from 2018.The results revealed that since the previous nationwide survey, liver cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis has decreased in Japan, while non-viral liver cirrhosis continues to increase.
This research was published in Hepatology Research, the English journal of the Japan Society of Hepatology.
Paper title
Etiological changes of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma-complicated liver cirrhosis in Japan: Updated nationwide survey from 2018 to 2021
Author of the paper
Hirayuki Enomoto (Gastroenterology (Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Medicine)) et al. (National Survey)
Research Background
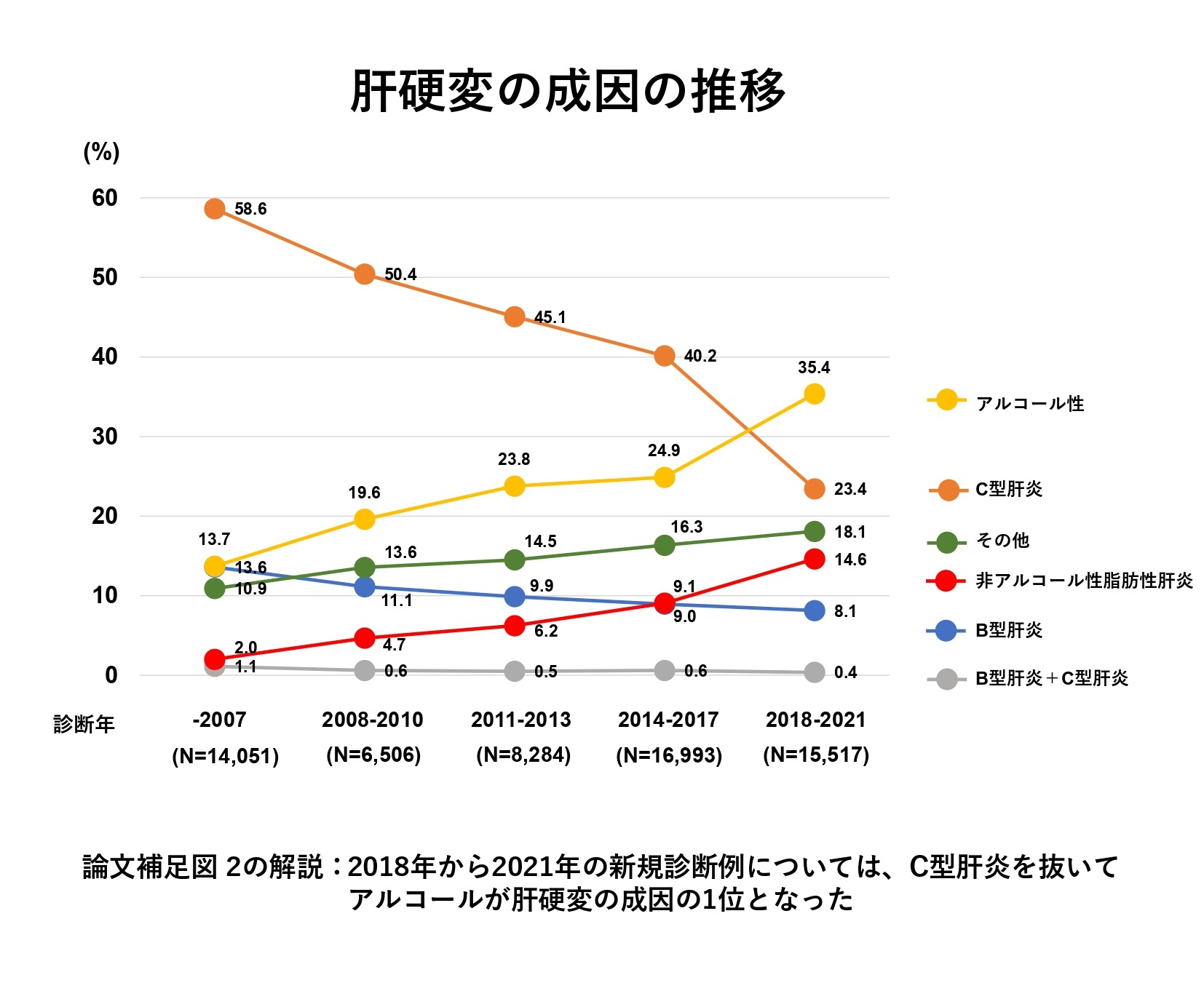
In Japan, it is believed that there are 1.5 to 2 million people infected with hepatitis B and C viruses, and hepatitis countermeasures have been implemented as a national project. In recent years, with the development of antiviral drugs, it has become possible to control the virus in the majority of cases. On the other hand, the number of liver diseases caused by lifestyle habits such as drinking alcohol and metabolic disorders is expected to increase. Against this background, it is expected that there will be a major change in the causes of chronic liver disease. A nationwide survey on the causes of liver cirrhosis conducted at the 54th General Meeting of the Japan Society of Hepatology in 2018 showed that liver cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis, which was 73.4% until 2007, has decreased to 49.7% since 2014, while non-viral liver cirrhosis has increased, with alcoholic liver cirrhosis increasing from 13.7% to 24.9% and liver cirrhosis caused by non-alcoholic steatohepatitis increasing from 2.0% to 9.1%. These results revealed that liver cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis is decreasing and non-viral liver cirrhosis is increasing in Japan (※1). Then, at the 59th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Hepatology held in 2023, we conducted a nationwide survey for the first time in five years.
Research Methods and Results
With the cooperation of 52 facilities that submitted abstracts for the 59th Annual Meeting of the Japan Society of Hepatology's Special Feature 1, "Poster Symposium: Causes and Pathological Changes of Liver Cirrhosis," we compiled data on the causes of newly diagnosed cases of liver cirrhosis between 2018 and 2021 at a total of 75 facilities nationwide. Ultimately, 15,517 cases were analyzed, with liver cirrhosis caused by hepatitis C and hepatitis B ranking second and fourth at 23.4% and 8.1%, respectively, while liver cirrhosis caused by non-viral alcohol and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis has increased, ranking first at 35.4% and third at 14.6%, respectively. In an accompanying analysis of cases with liver cancer, Hepatitis C remained in first place at 33.6%, but alcoholism came in a close second at 28.6%, followed by non-alcoholic fatty liver disease at 14.0% and Hepatitis B at 12.4%, again showing a decrease in viral liver disease and an increase in non-viral liver disease. These results make clear that the changes in etiology, such as a decrease in cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis and an increase in non-viral cirrhosis, have continued to progress since the previous survey.
Future challenges
In this survey report, we conducted a survey on the causes of liver cirrhosis as a whole and liver cirrhosis complicated with liver cancer with the cooperation of facilities nationwide, and were able to report on the trends. It is expected that the reversal of viral and non-viral causes of liver cancer will occur in the future, and we look forward to the results of the next survey.