Achievements
A paper on the elucidation of new reactivity of hypervalent iodine reagents has been published in the American Chemical Society journal "Organic Letters"
A collaborative research project between Lecturer Hiroyoshi Ezaki and Professor Kazuaki Fukushima of the Department of Chemistry, School School of Medicine, and Sakuya Shimizu, Atsushi Shibata, Ten Kano, Yuichi Kumai, Ryohei Kawakami, Lecturer Norihiro Tada, and Professor Akichika Ito of the Laboratory of Synthetic Pharmaceutical Manufacturing, Gifu Pharmaceutical University, has been published in the American Chemical Society's academic journal, Organic Letters (November 28, 2022) (DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c03648).
This research has made it possible to derive 4-imidazolidinones from diamides, including various peptide derivatives, using a highly reactive ethynyl hypervalent iodine reagent.
Topic
Synthesis of 4-Imidazolidinones from Diamides and Ethynyl Benziodoxolones via Double Michael-Type Addition: Ethynyl Benziodoxolones as Electrophilic Ynol Synthons
Author of the paper
Ayaka Shimizu, Atsushi Shibata, Takashi Kano, Yuuichi Kumai, Ryouhei Kawakami, Hiroyoshi Esaki*, Kazuaki Fukushima, Norihiro Tada* and Akichika Itoh*
Research Summary
New reactivity of hypervalent iodine reagents revealed, enabling molecular transformation of peptides
Research Background
4-Imidazolidinones are important structural components of pharmaceuticals and biologically active natural products, and are also used as organic catalysts and synthetic intermediates for various compounds. Although various synthetic methods for 4-imidazolidinones have been reported, most of them require reaction conditions such as strong acids or bases, high temperatures, or complicated procedures, so the development of a milder synthetic method is desired.
Research Methods and Results
In this study, we discovered that the highly reactive hypervalent iodine reagent TMS-EBX can be used to efficiently synthesize 4-imidazolidinone derivatives through the cyclization reaction of diamides containing various peptide derivatives (Figure 1).
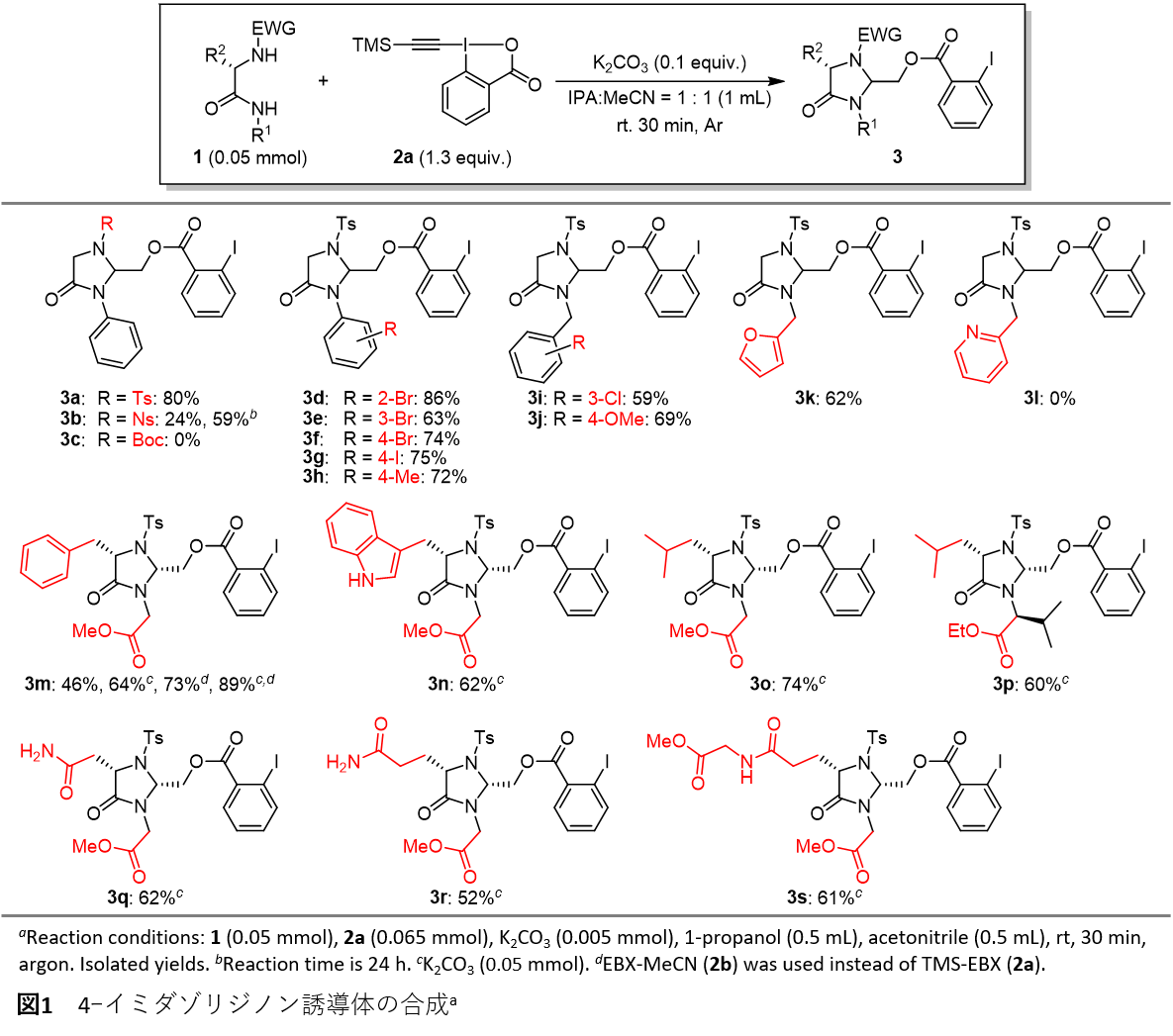
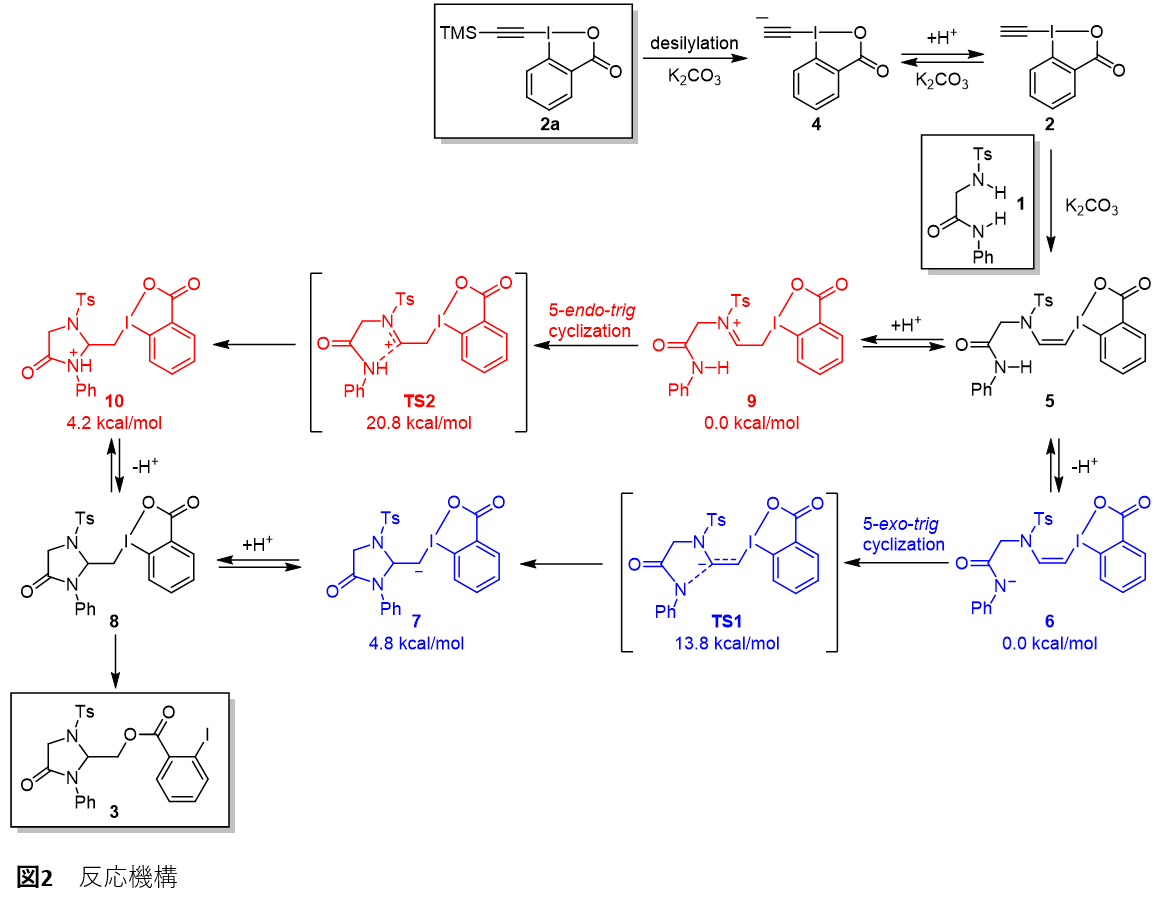
The synthesized 4-imidazolidinone can be converted into various peptide analogues by hydrolysis, Sonogashira reaction, deprotection, etc. In this reaction, a diamide having two nucleophilic sites is formed. 1 and EBX 2 This leads to a series of reactions that involve intermolecular and intramolecular addition reactions, ultimately giving 4-imidazolidinone. 3 It was inferred that the reaction was achieved by a Michael addition reaction between the two molecules. 5 from 8 The intramolecular cyclization reaction of 6 via 5-exo-trig It was revealed that the reaction likely proceeds via a cyclization mechanism (Figure 2).
Future challenges
This reaction proceeds efficiently under mild basic conditions, enabling the synthesis of peptide derivatives, which was previously difficult. It is anticipated that this method will be used to synthesize various heterocycles, contributing to the development of various pharmaceuticals and agricultural chemicals.
Source of research funds etc.
This research result is the result of collaborative research with Shimizu Ayaka, Shibata Atsushi, Kano Ten, Kumai Yuichi, Kawakami Ryohei, Tada Norihiro Lecturer, and Ito Akichika Professor from the Laboratory of Synthetic Pharmaceutical Manufacturing at Gifu Pharmaceutical University.