About the Corporation
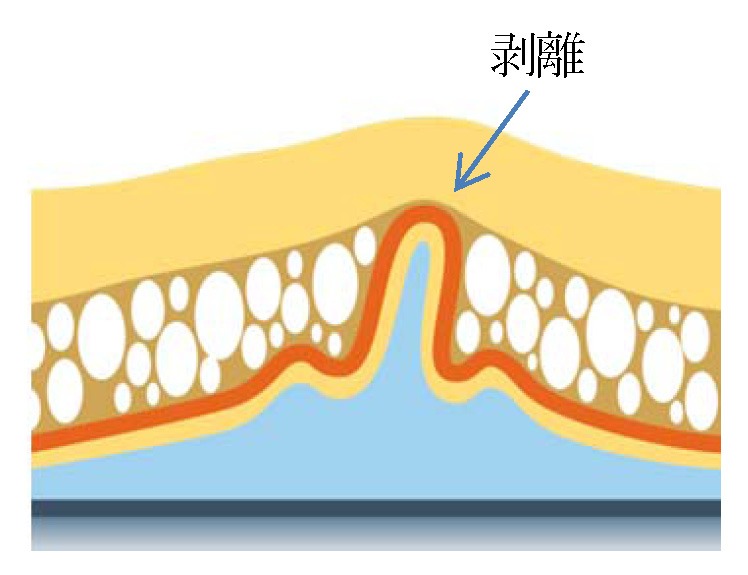
~After retinal detachment surgery~ Wrinkles in the eyeball cause distorted vision
A research group including Assistant Professor Hisashi Fukuyama and Chair Professor Fumi Gomi of the Department of Ophthalmology Hyogo Medical University (Nishinomiya City, Hyogo Prefecture, President Koichi Noguchi), in collaboration with Professor Tsuyoshi Okadome, Professor Takashi Kadosho, and Graduate Graduate School the Faculty of Science and Technology at Kwansei Gakuin University, quantitatively analyzed the wrinkles in the outer retina observed after surgery in patients who underwent vitreous surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. They also found that these wrinkles affect the distortion of vision (skewed vision), a postoperative aftereffect.
point
After retinal detachment surgery, all patients had wrinkles in the outer retina.
This is the first time that we have been able to prove numerically that wrinkles exist.
It turns out that the presence of wrinkles affects distortion of vision
A paper on the results of this research was published in the electronic version of Scientific Reports, an international scientific journal from the Nature Group, on Wednesday, February 20th at 7:00 p.m. Japan time (10:00 a.m. BST).
[Paper information]
・Magazine
“Scientific Reports” 20th, February, 2019 electronic version
・Article title
"Quantitative assessment of outer retinal folds on enface optical coherence tomography after vitrectomy for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment"
·author
Takashi Fukuyama, Hiromi Yagiri*, Keiji Araki, Hisashi Iwami, Yumiko Yoshida, Hiroto Ishikawa, Naoki Kimura, Takashi Kadoto*, Tsuyoshi Okadome*, Fumi Gomi
*Kwansei Gakuin University, School of Science and Technology *All departments except for those marked with an asterisk Department of Ophthalmology Hyogo Medical University
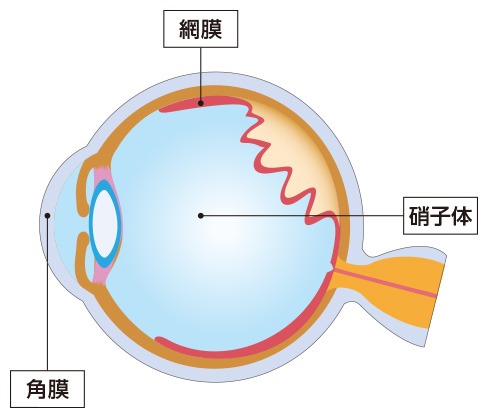
About rhegmatogenous retinal detachment
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is a disease in which a hole appears in the retina due to changes in the eyeball caused by aging, etc., and water in the eye passes through the hole and gets under the retina, causing the retina to detach. If surgery is not performed early, vision will not be restored. In vitreous surgery, gas is injected into the eyeball to hold down the detached retina, and a laser is used to close the hole and return the retina to its original state. The goal is to return the retina to its original position and restore vision, and there was not enough understanding of the distortion that occurs after surgery.
Research Methodology
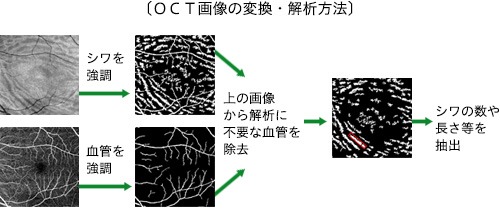
The study subjects were 33 patients aged 25 to 71 years who underwent vitreous surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment at Hyogo Medical University Hospital between October 2016 and August 2017. They used test data such as cross-sectional images of the eye taken with an enface OCT (optical coherence tomography) one month, three months, and six months after surgery, as well as M-CHARTS test results. They also analyzed the quantified data to investigate whether there was a correlation between wrinkles and distortion of vision.
Regarding the enface OCT images, collaborative researchers at the Faculty of Science and Technology, Kwansei Gakuin University, created a unique program to convert the images into images that are easier to analyze and clearly show the shape of wrinkles.

Takashi Fukuyama, Assistant Professor Department of Ophthalmology Hyogo Medical University
Researcher's Comments
In ophthalmology, image-based examinations are often used in daily practice to diagnose and treat patients. In this study, the images were analyzed and quantitatively expressed using numbers.
I had been interested in distortion of vision (skewed vision) for some time, and when I looked at images captured by a new imaging technology called enface OCT, I noticed folds in the outer retina of patients after retinal detachment surgery, so I began my research.
The results of this research also revealed that folds affect visual distortion, so in the future we would like to conduct research into practical and clinical aspects of how to reduce folds and make visual distortion less likely.