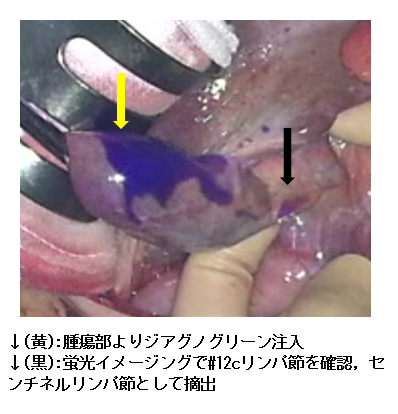
Identification of sentinel lymph nodes in gallbladder cancer by fluorescence imaging and elucidation of their clinical significance
Information updated: July 31, 2023
- Seeds Information
- Researcher Information
- What do you expect from collaboration with companies?
- Contact for this research
Seeds Information
keyword
Fluorescence imaging, sentinel lymph node
Field
Digestive Surgery
Overview
In this study, we will target patients scheduled to undergo extended cholecystectomy (hepatic bed hepatectomy, hepatic portal lymph node dissection) for gallbladder cancer (or gallbladder tumors with a high possibility of being gallbladder cancer), and will remove the lymph node (called the sentinel lymph node) to which the lymph flow from the gallbladder cancer reaches first and submit it for intraoperative pathological diagnosis, and compare the presence or absence of metastasis in this node with the results of definitive pathological diagnosis using permanently fixed specimens after surgery, with the aim of clarifying the accuracy of intraoperative rapid sentinel lymph node diagnosis. We will also investigate the relationship between the presence or absence of cancer metastasis to this sentinel lymph node and the presence or absence of metastasis to surrounding lymph nodes, and whether it is possible to identify the sentinel lymph node using fluorescent imaging technology using fluorescent dyes during gallbladder cancer surgery.
It is hoped that this study will clarify whether rapid intraoperative detection of sentinel lymph nodes during gallbladder cancer surgery can be useful in determining the extent of lymph node removal during gallbladder cancer surgery.
What's new?
To clarify whether intraoperative rapid diagnosis of sentinel lymph nodes during surgery for gallbladder cancer is useful for determining the extent of lymph node removal during surgery for gallbladder cancer.
What are its advantages over other studies?
To rapidly diagnose sentinel lymph nodes during surgery using a fluorescent imaging technique using a green dye called ICG, which has the property of remaining in tumors for a certain period of time.
What problem does it help solve?
Diagnosing the presence or absence of sentinel lymph node metastasis will enable individualized surgery for each case, and is expected to reduce unnecessary surgical invasion.
Possibility of other applications and developments
The method for identifying sentinel lymph nodes using fluorescent imaging technology may be applicable to other surgeries.
Related Patents
―
Related papers
- Lymph node dissection may be omitted in some cases of T2 gallbladder cancer if there is no metastasis to the cystic duct lymph nodes. PLoS One. 2021;16:e0247079.
- The concept of sentinel lymph node metastasis in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2015;102:1658-64.
- The identification rate of sentinel lymph nodes using ICG in esophageal cancer is 89%. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021;28:4869-4877.
Researcher Information
| full name | Seiko Hirono |
|---|---|
| Affiliation | Department of Gastroenterological Surgery, Faculty School of Medicine |
| Specialization | Digestive Surgery |
| Collaborative Researcher | Masayuki Okuno |
| Related links | Department website |
What do you expect from collaboration with companies?
We store resected specimens (frozen and paraffin-treated) of not only gallbladder cancer but also hepato-biliary-pancreatic cancer, making it possible to conduct collaborative research using these.
Contact for this research
兵庫医科大学 大学事務部 研究推進課
E-mail: chizai@hyo-med.ac.jp
Tel: 0798-45-6488

 Research Seeds Collection
Research Seeds Collection