脳傷害/梗塞病態に特異的に誘導される内在性幹細胞 (傷害/虚血誘導性幹細胞; iSC) を標的とした新規神経再生療法の開発
情報更新日 2025年12月26日
- Seeds Information
- Researcher Information
- What do you expect from collaboration with companies?
- Contact for this research
Seeds Information
keyword
脳梗塞、脳傷害、神経再生、幹細胞
Field
中枢神経系、再生医療、病態神経科学
Overview
近年、再生医療はめまぐるしく進歩しており、幹細胞を応用した再生療法の開発が期待されています。
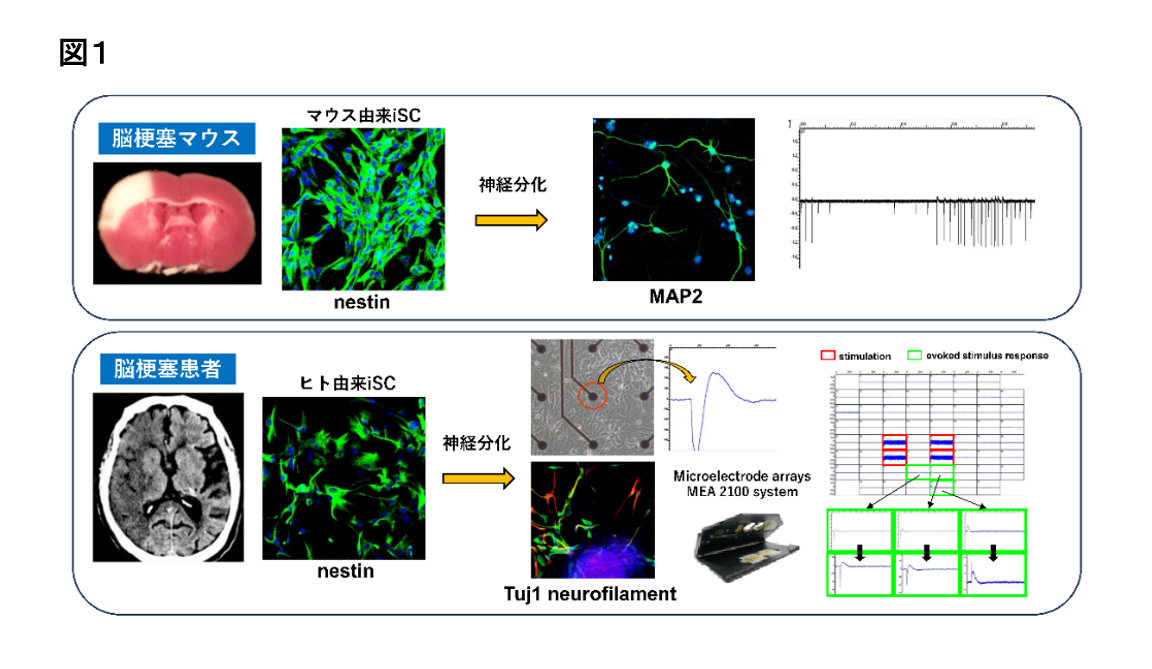
当部門では、脳傷害病態下に生体内に誘導される自己の内在性神経幹細胞の発掘を独自に試み、マウス脳梗塞巣(Eur J Neurosci, 29, 1842, 2009; Cells, 12, 2040, 2023)及び脳梗塞患者の梗塞巣(Stem Cells Dev, 26, 787, 2017)に、脳傷害病態時に特異的に誘導され、神経分化能を有する内在性幹細胞(傷害/虚血誘導性幹細胞;injury/ischemia-induced Stem/Progenitor Cell: iSC)が存在することを世界に先駆けて報告してきました(図1)。
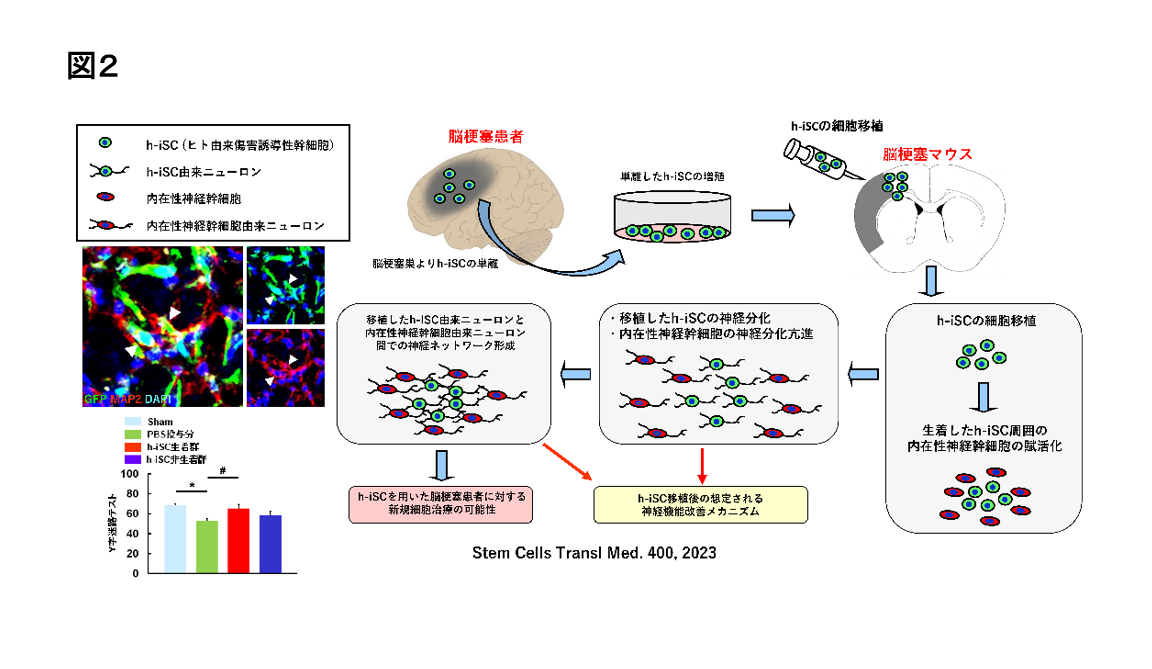
最近では、脳梗塞患者より単離培養したヒト由来iSCを脳梗塞マウスに細胞移植した前臨床試験を施行し(図2)、神経機能が改善すること(Stem Cells Transl Med, 12, 400, 2023)、その効果は同数の骨髄由来間葉系幹細胞(MSC)投与に比べ、より高いことを明らかにしました(Int J Mol Sci, 25, 12065, 2024)。
従って、iSCを標的とした研究は、脳梗塞などの脳傷害病態における新規細胞移植のソースとなり得るだけでなく、神経再生規定因子関連化合物の開発をはじめとし、内在性iSCの能力を最大限に活用することで、脳梗塞後に脱落した神経機能症状の回復を目指す治療戦略に展開可能です。
What's new?
従来は壊死した神経細胞と炎症担当細胞のみが存在すると考えられてきた脳梗塞巣内に、内在性の幹細胞(傷害/虚血誘導性幹細胞;iSC)が存在することをマウス(Eur J Neurosci, 29, 1842, 2009; Cells, 12, 2040, 2023)のみならずヒト(Stem Cells Dev, 26, 787, 2017)でも実証しました。
また、脳に存在する幹細胞として側脳室領域(SVZ)に内在性神経幹細胞が存在することが知られていましたが、iSCはSVZ由来神経幹細胞とは起源の異なる新たなタイプの幹細胞であることが明らかになりました (Int J Mol Sci, 22, 12997, 2021)。
さらに、iSCによる脳梗塞後の神経機能回復促進の可能性を⽀持する前臨床試験のデータも、最近、取得しました(Stem Cells Transl Med, 12, 400, 2023;Int J Mol Sci, 25, 12065, 2024)。
What are its advantages over other studies?
現在、細胞移植に用いられている他の種類の細胞 [MSCや人工多能性幹細胞 (iPS細胞) など] とiSCが決定的に異なるのは、iSCは脳傷害後の病態時の組織修復・再生過程で出現する内在性幹細胞であるという点です。
従って、iSCを標的とした研究では、神経再生規定因子関連化合物の開発をはじめとし、内在性iSCの能力を最大限に活用することで、脳梗塞後に脱落した神経機能症状の回復を目指す治療戦略に展開可能です。
その治療法は、脳への細胞移植に伴うリスク回避だけでなく、細胞移植に必要な特別な設備や施設を必要としないことから、非常に合理的であると同時に世界初の脳の自己修復プログラムに則した神経再生の試みであり、高い国際競争力を有します。
What problem does it help solve?
脳梗塞後の神経再生を介した神経機能回復
Possibility of other applications and developments
iSCは脳梗塞のみならず、脱髄性の中枢神経疾患(Cells, 8, 1025, 2019)や脊髄損傷(Stem Cells Dev, 31, 555, 2022)においても、病変部に誘導されることが既に明らかになっています。
従って、脳梗塞をはじめとし、多発性硬化症や外傷性神経疾患(脳挫傷、脊髄損傷)など、様々な中枢神経疾患に対して世界初となる新規神経再生促進剤として臨床応用される可能性があります。
Related Patents
Patent No. 4481706: Title of invention: "Cerebral infarction disease model mouse"
Related papers
- Nakagomi T, et al. Isolation and characterization of neural stem/progenitor cells from post-stroke cerebral cortex in mice. Eur J Neurosci, 29, 1842-1852, 2009.
- Tatebayashi K, et al. Identification of multipotent stem cells in human brain tissue following stroke. Stem Cells Dev, 26, 787-797, 2017.
- Nakagomi T, et al. Transplantation of human brain-derived ischemia-induced multipotent stem cells ameliorates neurological dysfunction in mice after stroke. Stem Cells Transl Med, 12, 400-414, 2023.
- Tanada S, et al. Human-brain-derived ischemia-induced stem cell transplantation is associated with a greater neurological functional improvement compared with human-bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in mice after stroke, Int J Mol Sci, 25, 12065, 2024.
- Nakagomi T. Unlocking the potential of regionally-activated injury/ischemia-induced stem cells for neural regeneration. Stem Cells, 43, sxaf015, 2025.
Researcher Information
| full name | Takayuki Nakagomi |
|---|---|
| Affiliation | School of Medicine Institute for Advanced Medical Sciences Laboratory of Neural Repair and Regeneration |
| Specialization | 中枢神経系、再生医療、病態神経科学 |
| Collaborative Researcher | Akiko Doi |
| Related links | Course introduction website |
What do you expect from collaboration with companies?
当部門は世界に先駆けて、脳梗塞マウスのみならず、脳梗塞患者の梗塞巣より、iSCの単離、樹立に成功しており、国際的にiSCに関するパイオニア的立場にあります(Stem Cells, 27:43, sxaf015, 2025)。
また、iSCに関する研究は、日本脳循環代謝学会のエビデンス創出・基礎研究推進委員会による認定研究(2018年度、2019年度、2024年度、2025年度)にも選出されてきた実績があります。
当部⾨では、脳梗塞巣より単離・樹⽴したiSCをストックしており、貴社の有する薬剤や化合物などが、iSCに対していかなる効果(iSCに対する増殖能や細胞保護作⽤の評価、iSCの神経分化能の評価など)を有するかを調べることが可能です。
当部門では、これまでに複数の製薬会社と創薬開発に関する共同研究や特許出願を行ってきた経験もあり、本研究を通してヒット化合物の同定など新たな発見がみつかった場合は、創薬開発の共同研究を提案させていたくと同時にすみやかに特許申請を行い、知財化を行うことも可能です。
Contact for this research
兵庫医科大学 大学事務部 研究推進課
E-mail: chizai@hyo-med.ac.jp
Tel: 0798-45-6488

 Research Seeds Collection
Research Seeds Collection